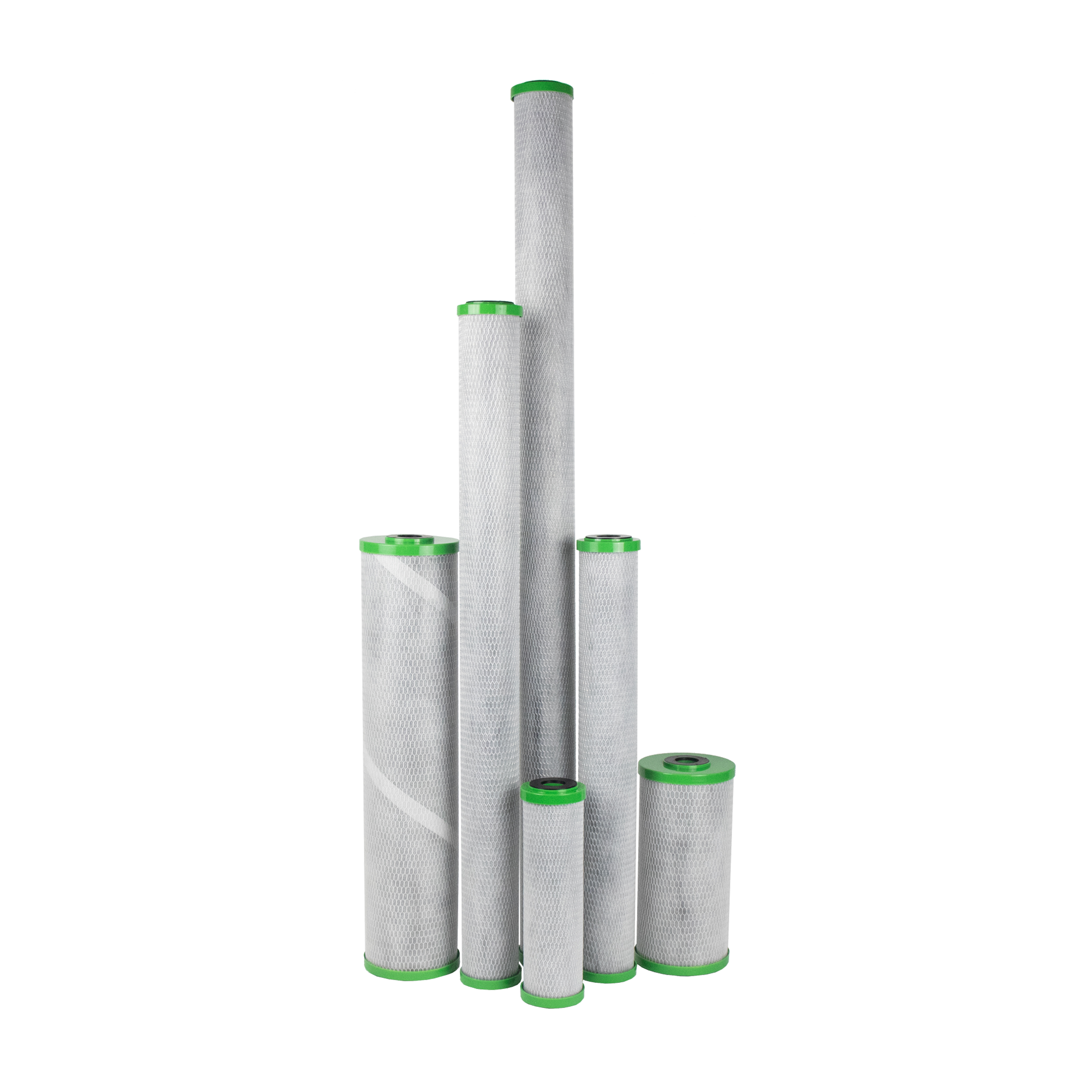
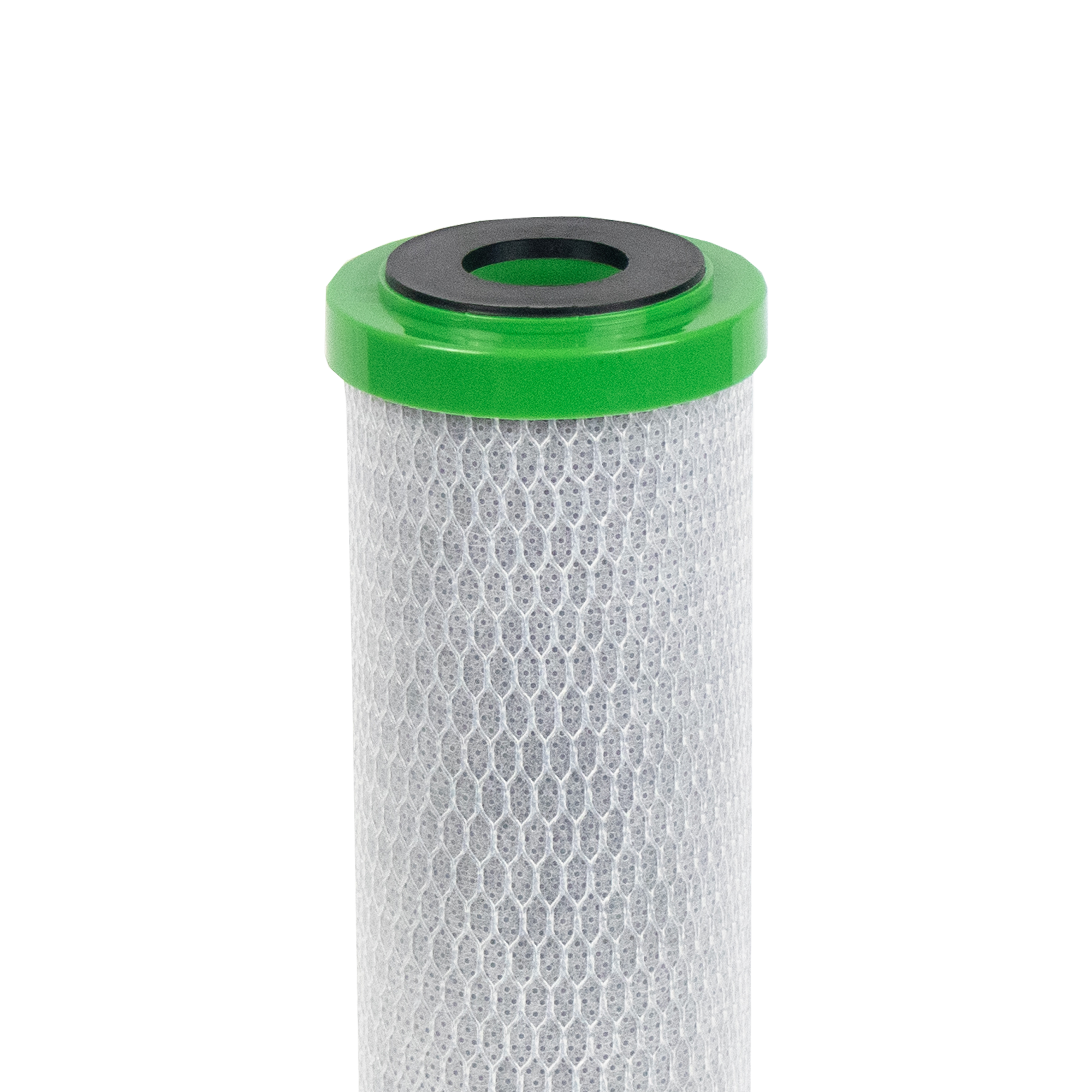
FibreOnyx Lead Reduction Carbon Filter (SFBC-PB)
- Excellent lead reduction
- Simultaneous CTO reduction
- NSF-53 Certified for Giardia Cyst reduction
- Low pressure drop
- Antimicrobial agent applied to prevent bacterial growth
- Gaskets permanently moulded onto end-caps to prevent dislodging
- Point of use drinking water from borehole feed
- Drinking water in aged pipework and closed loop systems
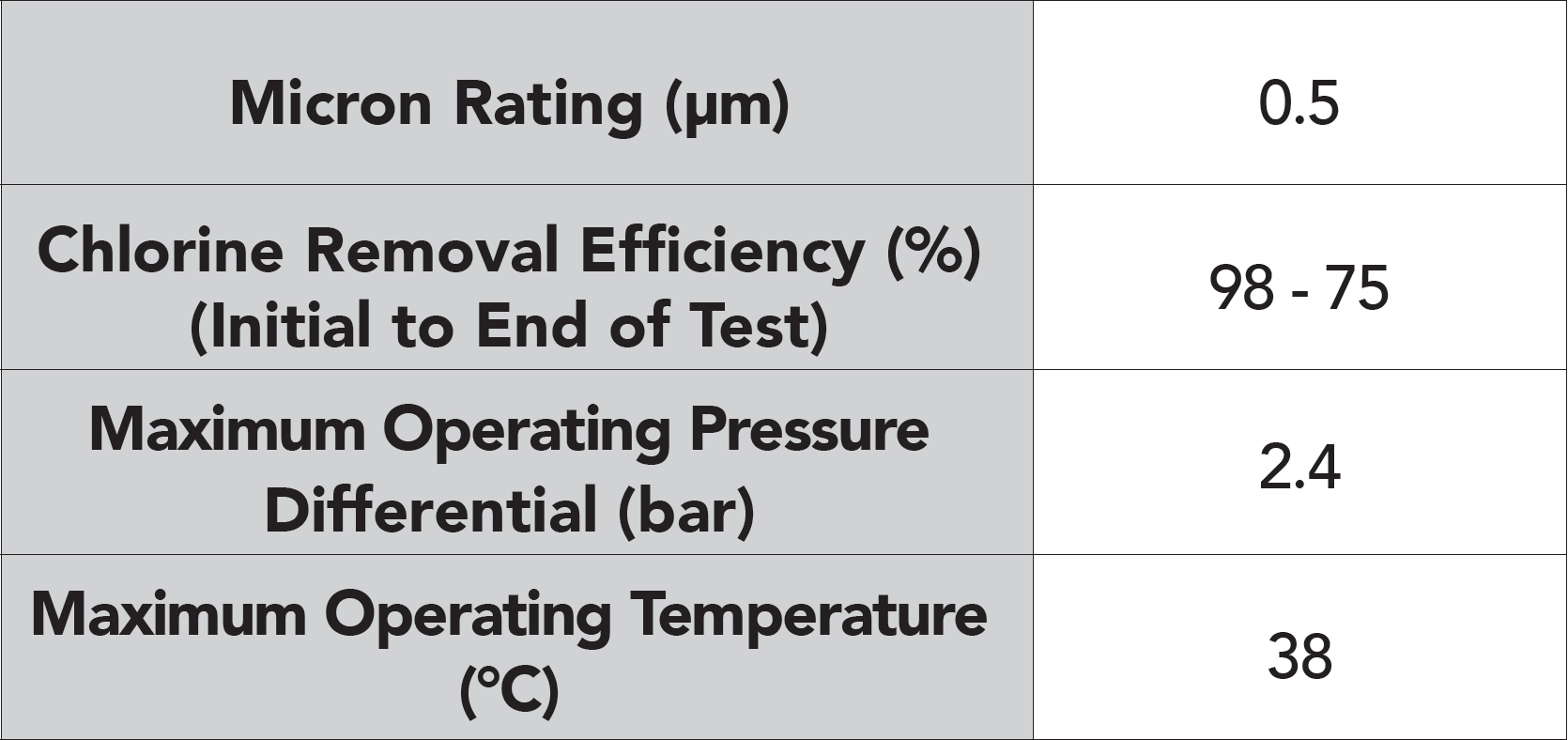
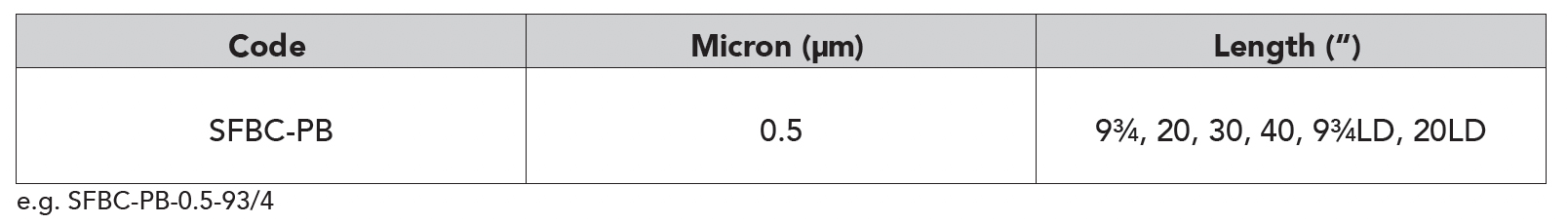
Features & Information
Exceptional lead removal without compromise on chlorine control. The SFBC-PB incorporates a post-filtration layer to eliminate fine release and is comprised of NSF53-certified media to reduce Giardia cysts.
FAQs - SFBC-PB
The SFBC-PB provides four times higher lead removal compared to the industry standard. It is ideal for use in areas with soft water or borehole feeds with lead piping. The standard SFBC cartridge offers chlorine removal capabilities similar to the SFBC-PB.
The replacement frequency depends on water quality and usage. Generally, it is advisable to replace the cartridge as per the manufacturer’s recommended service life, which can vary. For the SFBC-PB, this is typically around 6-12 months, but it may vary based on water conditions.
Removing lead from your water supply is crucial for several important reasons:
- Health Concerns: Lead is a toxic heavy metal that poses significant health risks, particularly to children and pregnant women.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many countries have stringent regulations regarding the allowable levels of lead in drinking water.
- Water Quality and Taste: Water that contains lead may have a metallic taste or unpleasant odour, making it unappealing for consumption or for use in cooking and preparing beverages.
- Infrastructure Protection: Lead can corrode plumbing and water distribution systems, causing damage and leading to costly repairs.
Carbon filters work by utilising activated carbon, a highly porous material with a large surface area. When water passes through the carbon filter, contaminants come into contact with the activated carbon. The contaminants are either adsorbed onto the carbon’s surface or undergo chemical reactions that neutralise them. This process effectively removes impurities such as chlorine, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), odours, and some heavy metals, resulting in cleaner and purer water.



