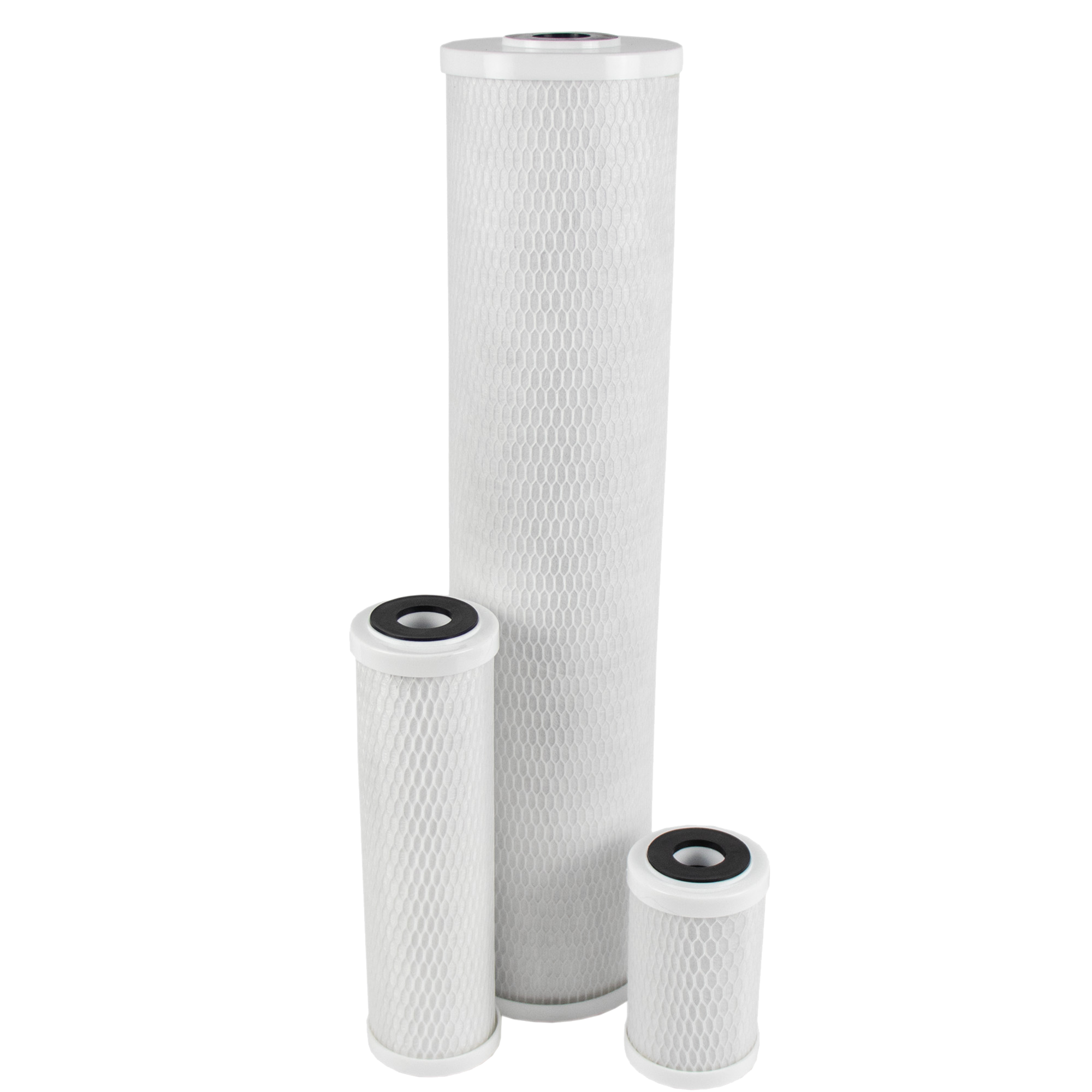
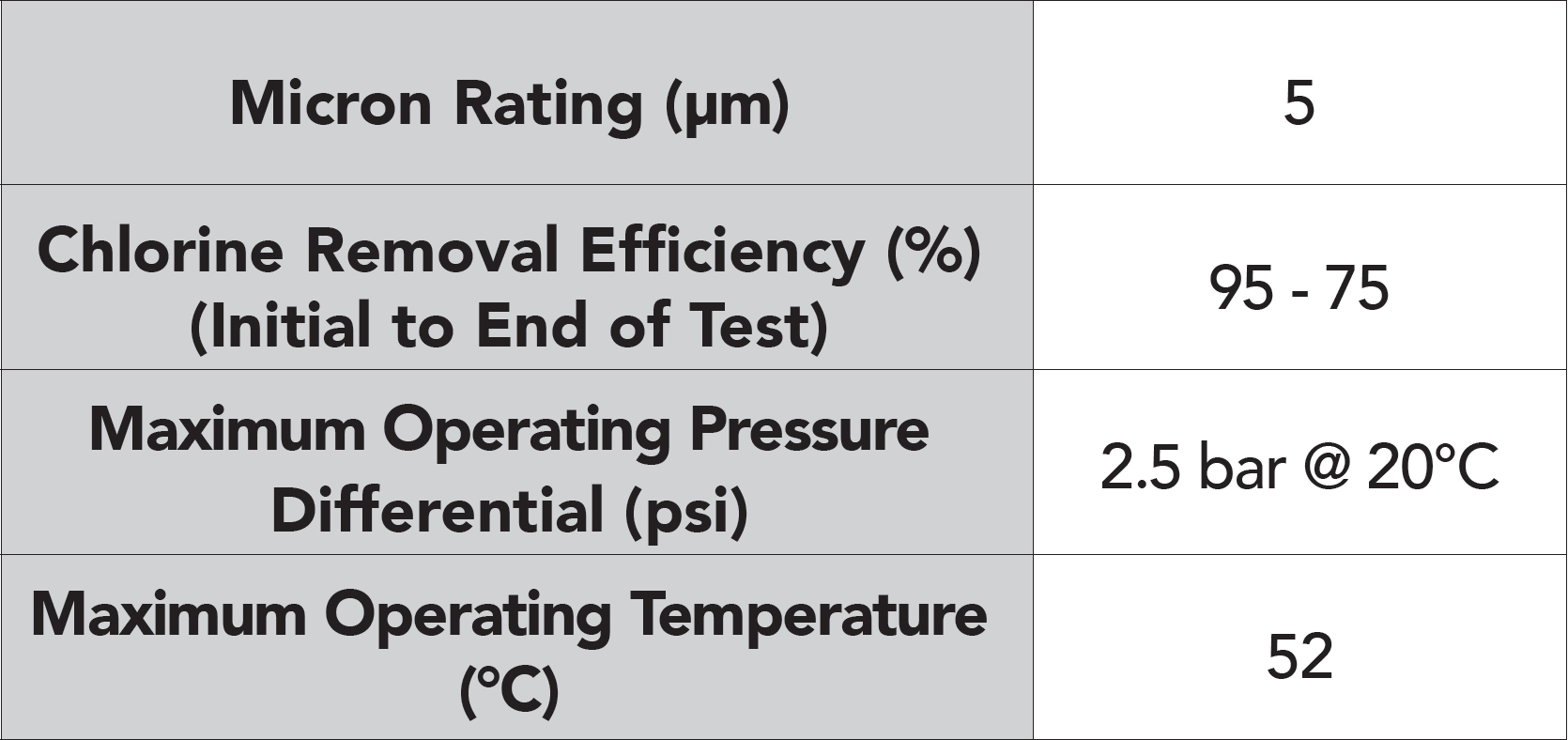
870 Standard Carbon Block (SCB)
- Extruded from high quality carbon fines, the SCB has a much higher adsorption capacity, extending life and improved chlorine reduction capacities, over the ECB
- The fine, acid-washed bituminous, powdered activated carbon (PAC) used in the SCB results in a highly efficient carbon cartridge with sediment filtration capabilities
- Constructed with an outer polypropylene wrap that protects and extends the life of the carbon block, capturing particles and preventing premature plugging
- Food grade additives used to bond the PAC
- Available in large diameter 9¾” and 20″ lengths for reduced cartridge changeout frequency
- Drinking water
- VOC reduction
- THM reduction
- RO protection

Features & Information
A low ash, microporous coconut carbon cartridge, favoured for drinking water and beverage applications where chloramines are not present.
FAQs - SCB
Refers to the distinctive flavour and smell associated with chlorine in water. Chlorine is commonly used as a disinfectant in water treatment processes to kill bacteria, viruses, and other harmful microorganisms. While chlorine is effective in reducing waterborne pathogens it can leave a residual taste (often described as a bleach-like or chemical flavour) and odour in the treated water.
Removing chlorine from water is often desired for several reasons:
- Taste and Odour: chlorine causes an unpleasant taste and odour in water.
- Beverage and Food Quality: natural flavours and characteristics are compromised by the presence of chlorine, specifically yeast.
- Cosmetic and Aesthetics: Chlorine can strip the natural oils from the skin and hair, leading to dryness and potential damage.
- Disinfection Byproducts: Chlorine can react with naturally occurring organic matter in water, forming disinfection byproducts such as trihalomethane and halo-acetic acids. Long-term exposure has been associated with potential health risks, such as cancer.
- Improved Taste and Odour: Removes unpleasant tastes and odours from water, making it more enjoyable to drink and cook with.
- Chlorine Removal: Highly effective at removing chlorine and its byproducts from water.
- Chemical Filtration: Reduces or removes various chemical contaminants from water.
- Adsorption of Contaminants: Activated carbon has a large surface area and porous structure, allowing it to effectively adsorb a wide range of impurities.
- Versatility: Used in a variety of applications, including residential, commercial, and industrial settings.
- Cost-Effective Solution: Carbon filters offer a cost-effective filtration solution compared to other complex filtration technologies.
Carbon filters work by utilising activated carbon, a highly porous material with a large surface area. When water passes through the carbon filter, contaminants come into contact with the activated carbon. The contaminants are either adsorbed onto the carbon’s surface or undergo chemical reactions that neutralise them. This process effectively removes impurities such as chlorine, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), odours, and some heavy metals, resulting in cleaner and purer water.



